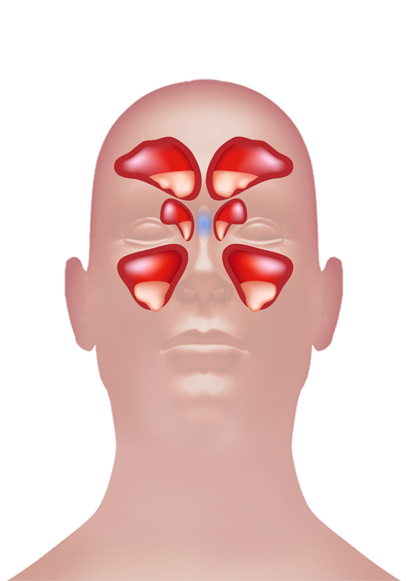
Sinus Frontalis
Sinus Frontalis is the Latin pronunciation for the Frontal Sinus. These Frontal Sinuses are situated behind the Brow ridges (Superciliary Arches). These sinuses are Mucosal (lining covered in Epithelium) lined airspaces present in bones of skull and face. Each of these sinuses opens up into the anterior of the Middle Nasal Meatus (Nasal opening) of nose through Frontonasal Duct (passage between Frontal Air Sinuses and corresponding nasal cavity). These structures then open into the Middle Meatus Hiatus Semilunaris (crescent shape groove in lateral wall of nasal cavity).
read more Sinus Frontalis Superior Nasal ConchalInferior Nasal Concha Nasal CavitySinus Sphenoidalis Alveoli Larynx Nasopharynx
Oropharynx Laryngopharynx Frontal SinusSphenoid SinusEthmoid Sinus Maxillary SinusBronchus Vertebrate Trachea Bronchioles Capillary Beds
Alveolar Duct Alveolar Sacs Pulmonary VeinPulmonary Artery
Sinus Frontalis
ANATOMY
Frontal Sinuses are sometimes symmetrical and the Septum (wall dividing cavity into smaller ones) in between them often changes it side to one or another side of the middle line. The average length of these sinuses is 28mm, breadth 24mm, depth 20mm.
INNERVATION
Supraorbital Nerve innervates the Mucous membrane in the sinuses. These nerves carry Postganglionic Parasympathetic Nerve fibers from Ophthalmic Nerve for mucous secretions.
BLOOD SUPPLY
Blood supply to these sinuses is supplied through Supraorbital Artery and Anterior Ethmoidal Artery.
FUNCTION
It is essential for the air filtration carried out by nose through its mucus production. Provided with immune cells, antibodies and antibacterial proteins in abundance, the thick upper layer of nasal mucus entraps bacteria and small particles in tissues. The layers beneath are thin and provide a substrate through which the Cilia are able to move the upper layer with the debris to the Choanae (posterior Nasal Apertures).
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
One of the common pathologies of Frontal Sinus is Sinusitis. Fractures range from anterior table fractures to complex fractures which involve Frontal Recess, Orbits, skull base and intracranial contents.
Report Error