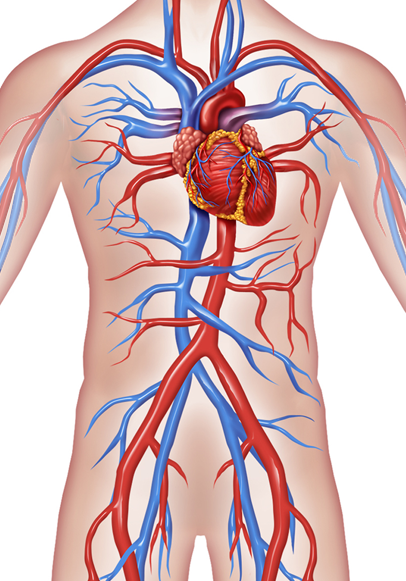
Circulatory System of the Torso
The process of blood flow through the body is called circulation. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen away from the heart. The veins carry oxygen poor blood back to your heart. The cardiovascular structures for the blood flowing to the torso, arms and other extremities is a closed cardiovascular system (comprised of the heart, the arteries, and the veins) which keeps the blood in the circulatory system as it moves it toward or away from the heart.
read more Superficial Temporal Artery Internal Carotid ArteryExternal Carotid Artery Common Carotid Arteries Subclavian Artery Superior Vena CavaPulmonary Arteries HeartInferior Vena Cava Common Iliac Artery Aorta Descending Aorta
Common Iliac Vein Subclavian VeinAxillary Vein Axillary ArteryBrachial Artery Ulnar Artery Radial Artery Basilic VeinInternal Iliac Artery External Iliac VeinExternal Iliac Artery Great Saphenous Vein Femoral Artery Femoral Vein
Tibial Arteries Small Saphenous Vein Tibial Veins
Circulatory System of the Torso
In the human circulatory system, we have a double circulation because there is a separate pulmonary circuit to the lungs and a systemic circuit to the body. These arteries and veins lie close to each other and are involved it countercurrent heat / cool exchanges.
The cardiovascular system in the torso part of the body uses both the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit to deliver oxygenated blood to tissues and organs and take from the tissues and organs blood depleted of oxygen. A closer look at how the pulmonary circuit to the lungs work demonstrates how the reverse of the systemic system, in which the arteries are delivering oxygenated blood and the veins are taking away oxygen depleted blood, is true of the pulmonary circuit. The following points show how this pulmonary circuit system operates.
Pulmonary Circuit :
The circulation of blood through vessels to the heart and away from the heart works the opposite of the closed blood systemic system that delivers and takes away blood to the rest of the body. In pulmonary circulation the roles are switched.
-
The pulmonary artery takes oxygen poor blood to the lungs.
-
The pulmonary vein sends oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
The torso includes the area of the body from the shoulders to the lower abdomen and pelvic region of the body before the lower extremities are evident. This excludes the head and the limbs. Each of these vessels carry oxygen-rich blood throughout the torso.
Circulation of oxygen-rich blood in the Torso:
-
Arch of the aorta
-
Pulmonary vein (to the heart)
-
Thoracic aorta
-
Abdominal aorta (splits to go to each extremity)
Each of these vessels carry oxygen-depleted blood throughout the torso.
Circulation of oxygen depleted blood in the Torso:
-
Pulmonary artery (to the lungs)
-
Inferior vena cava (splits to go to each extremity)
Report Error