Colitis
Definition of Colitis
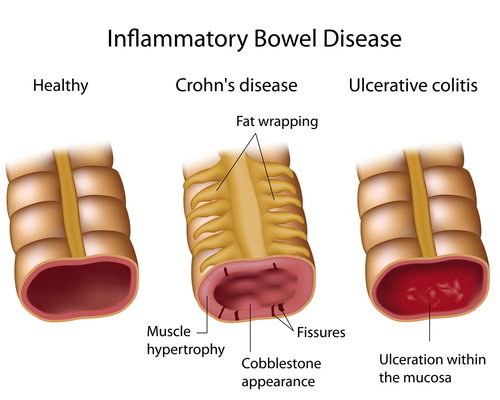
Colitis is an inflammation of the colon and this term is more commonly used for the inflammation of the large intestine (which consists of colon, caecum and rectum). Colitis may sometimes be applied to Crohn’s disease if the diagnosis is not known, i.e. when the cause is undetermined. On the other hand when the diagnosis is clear, it is usually ulcerative colitis.
Cause of Colitis
There are a number of different causes of colitis which include the following:
-
Viral and parasitic infections
-
Food poisoning due to bacteria
-
Inflammatory disorders like ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease
-
Insufficient blood supply that leads to ischemic colitis
-
When the large intestine has been exposed to radiations in the past
-
Autoimmune conditions
-
Genetic causes
-
Environmental factors (poor hygiene, pollution and certain diets)
Signs and Symptoms of Colitis
There are many variable signs and symptoms of colitis depending on the cause and factors that modify it. These include:
-
Abdominal pain
-
Bloating of abdomen
-
Loss of appetite
-
Weight loss
-
Fatigue
-
Fever
-
Chills
-
Cramping
-
Bloody stools
-
Mucus in stool
-
Diarrhea
-
Dehydration
-
Constant urge to defecate
-
Abdominal tenderness
-
Redness (erythema) of inner surface of colon when seen on colonoscopy
Diagnosis of Colitis
The diagnosis is based on good medical history and examination. Various techniques and instruments are used for its diagnosis, of which colonoscopy is the method of first choice. In this method a flexible tube is inserted into the rectum and specific areas of the colon are visualized. Biopsy taken during this test may reveal inflammatory changes.
Other tests include:
-
Abdominal CT scan
-
Abdominal MRI
-
Abdominal X-ray
-
Barium enema
Prevention from Colitis
The lack of clean drinking water and adequate sanitation, poor hand washing and poor kitchen hygiene allow the potential for infectious colitis. Cleanliness is important to prevent it.
Inflammatory bowel diseases are difficult to prevent because it is caused by heredity.
Since ischemic colitis is caused by narrowing of the blood vessels to the bowel, decreasing the risks for other types of circulatory problems such as peripheral vascular disease, heart attack, and stroke will also decrease the risk for ischemic colitis. To prevent it, quit smoking, control high blood pressure, keep cholesterol at healthy levels.
Treatment of Colitis
The treatment of colitis is directed against the symptoms of the disease and can be achieved by the combination of the following three ways:
-
Medication
Medication is used for the inflammation and to fight against various infections. It is also used to relieve the signs and symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea.
-
Diet and Nutrition
As the food we eat may be a risk factor for colitis if the quality of food is bad, the choice of food can help against the disease. Soft bland foods rich in fiber like leafy vegetables and fruits are very good as they improve our bowel movements. Good quality proteins and carbs are also needed.
-
Surgery
When the medical treatment does not produce fruitful results, surgical intervention may be needed. This procedure involves the removal of inflamed part of the colon (colectomy). However there are chances of recurrence in Crohn’s disease. On the other hand ulcerative colitis is cured once the colon is removed.
