Kidney Stone
Definition of Kidney Stone
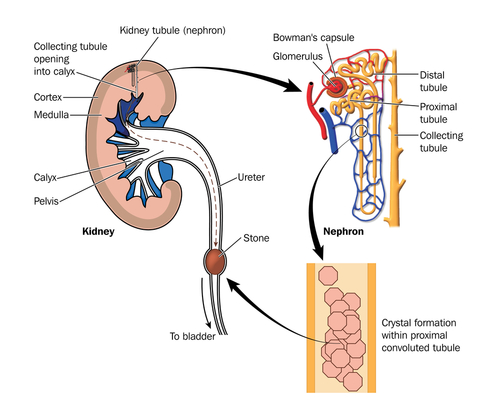
Also known as Renal Calculus, Kidney Stone is a solid crystal aggregation in kidneys. It is caused due to deposition of dietary minerals in urine. A kidney stone is usually made up of small calcium and oxalate crystals in part of kidney where urine is collected (renal pelvis). It usually causes little problem until stone falls into ureter causing an obstruction. This prevents drainage of urine and causing severe pain.
Depending upon the location within urinary tract kidney stones have following names .
-
Urolith, stone located anywhere in urinary tract.
-
Nephrolith, stone within kidney.
-
Ureterolith, stone within ureter.
Cause of Kidney Stone
Kidney stones have no definite single cause but many factors increase the risk. One of the main causes for kidney stone is that urine contains crystal forming substances like Calcium Oxalate and Uric Acid. Also one of the causes is the presence of substance that keeps crystals stick together. Following are some of the causes based on the types of kidney stones.
Calcium Stones:
Mostly kidney stones are calcium stones. They are in form of Calcium Oxalate. Dietary factors, high doses of vitamin D, intestinal bypass surgery and metabolic disorders are some of the causes to increase concentration of oxalate in urine. Calcium stones can also be in form of Calcium phosphate.
Struvite Stones:
Struvite stones are caused in response to urinary tract infections. These stones grow quickly with little symptoms. The main causative agent of struvite stones is the bacteria named proteus species.
Uric Acid Stones:
Uric acid stones are caused due to minimum fluid consumption and intake of high protein diet. Gout is also another cause for it. Genetic factors also are responsible for uric acid stones.
Cystine Stones:
The cause for Cystine stones is hereditary disorder. This causes kidney to excrete certain amino acids like Cystinuria.
Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Stone
Pain caused due obstruction of ureter or renal pelvis by Kidney Stones is excruciating. The pain is intermittent and rotates from groin to inner thigh. This particular pain is called Renal Colic. This is one of the main pain sensations. Other symptoms that are accompanied with this are as follows.
-
Urinary urgency
-
Restlessness
-
Hematuria
-
Sweating
-
Nausea
-
Vomiting
A kidney stone may not cause pain until it moves in kidney or pass in ureter. At that point symptoms are following.
-
Pain below ribs, in sides and back.
-
Pain in lower abdomen and groin
-
Pain in waves
-
Pain on urination
-
Red or brown colored urine
-
Fever and chills
The pain seems to shift to different location or increase as stone moves through urinary tract.
Risk Factors for Kidney Stone
Following are some of the risk factors for kidney stones.
Being a man:
Men are normally at more risk for developing kidney stones than women. Nearly 80% men are patients of kidney stones.
Being an adult:
Although kidney stones can occur at any age but normally the people of 40 years of age are more likely to be at risk for developing kidney stones.
Family history:
The people who have persons having kidney stones in their family are more likely to be at risk. Also if someone has suffered from kidney stones once he or she can be at risk too.
Dehydration:
People who don’t drink plenty of fluids are a t risk for kidney stones. Also people living in hot climate areas are also at risk.
Obesity:
High body mass index (BMI), large waist size and weight gain are the risk factors for developing kidney stones.
Medical conditions:
Diseases that increase risk for developing kidney stones are as follows.
-
Renal tubular disease
-
Acidosis
-
Cystinuria
-
Urinary tract infections
Diagnosis of Kidney Stone
Patients suffering with renal colic pain exhibit classic symptoms of pain, writhing and vomiting. The doctor can make diagnosis based on history and brief physical examination. Physical examination is carried out to check tenderness in flank where kidney is located. The physical exam is carried out to check other problems that include the following.
-
Appendicitis
-
Gallbladder diseases
-
Diverticulitis
-
Aneurysm
One of the diagnostic procedures is Urinalysis. This is performed to check blood in urine and also white blood cells or bacteria that may be cause for an infection.
Imaging is also taken of the patients. Following are the available two procedures.
-
CT scans: It is the most reliable way for detecting kidney stones. The advantage of this imaging is that location and size of the stone is known. This helps in treatment. It has only one risk and that is of radiation.
-
Ultrasound: This imaging includes location of stones in kidneys, ureter and bladder. Swelling of kidney exhibit obstruction from stone and is visible by this imaging.
Prevention From Kidney Stone
Prevention of the kidney stones depends upon their types. Those having calcium stones must drink lots of water whereas those with High Uric Acid must use Thiazide diuretics and Citrate. Following are the steps for prevention.
-
Dietary measures:
Diet can have influence on formation of kidney stones. Prevention strategy is to include dietary modifications and medications with the main purpose to excrete calculogenic compounds. Some of these dietary measures are as follows.
-
Increase fluid intake
-
Intake of citrate rich drinks
-
Limit consumption of soft drinks which contain Phosphoric Acid.
-
Urine Alkalinization:
The main prevention against kidney stones is to increase alkalinization (pH) of urine.
-
Medications:
One of the recognized therapies for prevention against kidney stones is the use of the following drugs.
-
Thiazide
-
Thiazide like Diuretics
-
Chlorthalidone
-
Indapamide
Treatment of Kidney Stone
The treatment for various conditions associated with kidney stones are as follows.
For Renal Colic Pain:
The treatment included for renal colic is pain control and hydration. If the pain is severe then patient must be taken to emergency unit for intravenous medication that includes narcotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and medicines to control vomiting. Patient is prescribed Tamsulosin that relaxes the urinary tract and promote stone and urine passage.
For Uncomplicated condition:
The stones are passed to allow in uncomplicated conditions. The stones pass on in 2 to 3 weeks.
Lithotripsy
Lithotripsy is a physical destruction of any hardened mass inside the body. There are different types of lithotripsy like electromagnetic and endoscopic lithotripsy etc but LASER lithotripsy is an effective method to remove kidney stones.
For other diseases:
Patients suffering with other diseases developed by kidney stones are treated by placing a stent or Nephrostomy to prevent increase in infection.