Meningitis
Definition of Meningitis
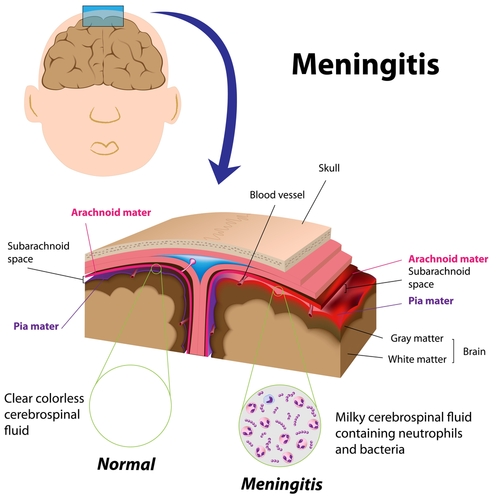
Meningitis is the combination of two words: meninges= membranes and itis= inflammation. So meningitis is nothing but the inflammation of the membranes covering brain and spinal cord. This condition is very dangerous due to the close proximity of the pathology of the disease to vital body parts like brain and spinal cord. That’s why meningitis is always treated as a medical emergency.
Cause of Meningitis
Following are the most important causes of meningitis:
-
The most important cause of meningitis is bacterial infection. The causative bacteria differ among individuals of different age groups or under different conditions:
-
In the case of infants and premature babies the most important cause of bacterial meningitis are Listeria monocytogenes, E.Coli and group B streptococci.
-
Children under the age 5 are mostly affected by H.Influenzae type B bacteria.
-
Older children are commonly affected by two bacteria namely N.Meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
-
In adults aged below 50 H.Influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae are the most important cause of bacterial meningitis.
-
In adults aged above 50, Listeria monocytogenes is the basic cause of bacterial meningitis.
-
Staphylococci and Pseudomonas species are responsible for causing meningitis in patients with impaired immune system.
-
Tuberculous meningitis is a type of meningitis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in patients with impaired immune system.
-
-
Second most important cause of meningitis is viral infections. The most important viruses that cause meningitis include:
-
Enterovirus.
-
Varicella zoster virus.
-
Mumps virus.
-
HIV.
-
Herpes simplex type 2 virus.
-
LCMV.
-
-
Fungal infections can cause meningitis in immunocompromised patients. The strains of fungus responsible for causing meningitis include:
-
Cryptococcus neoformans.
-
Candida.
-
Histoplasma capsulatum.
-
Blastomyces dermatidis.
-
Coccidioides immitis.
-
-
Parasites responsible for causing meningitis include:
-
Schistosoma.
-
Gnathostoma spinigerum
-
Angiostrongylus cantonensis
-
-
Non-infectious causes of meningitis include:
-
Cancer spread.
-
Drug reactions.
- Inflammatory causes like sarcoidosis.
-
Signs and Symptoms of Meningitis
Following are the most important signs and symptoms of meningitis:
-
 Fever.
Fever. -
Chills.
-
Change in mental status.
-
Nausea and vomiting.
-
Stiffness of neck.
-
Photophobia.
-
Headache.
-
Rapid breathing.
-
Unusual posture.
-
Agitation.
Risk Factors for Meningitis
Following are the most important risk factors:
-
Infants and elderly.
-
Over crowding.
-
Poor immune system.
-
Travelling to areas with higher parasitic and bacterial burdens.
- Use of certain medicines.
Diagnosis of Meningitis
Diagnosis includes:
-
Complete history.
-
Examination.
-
Further investigations like lumbar puncture, MRI.
Treatment of Meningitis
Treatment includes:
-
Antibiotics for bacterial meningitis.
-
Antiviral for viral meningitis.
-
IV fluids to make up for fluid loss.
