Ovarian Cyst
Definition of Ovarian Cyst
An Ovarian Cyst is defined as any collection of fluid surrounded by thin wall within ovary, which is larger than about 2 cm. Ovarian Cysts occur in women of all ages and more frequently in females of childbearing age.
Ovarian Cysts are of two types :
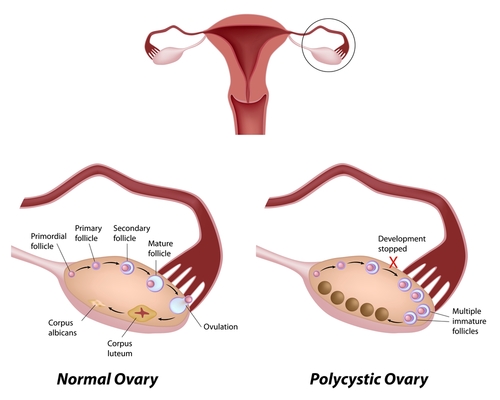
- Functional Ovarian Cysts : These are part of normal menstrual cycle and can arise from any part playing a role in the cycle. For example Ovarian Follicles are a normal part of the ovaries playing major role in menstrual cycle. However an Follicle larger than 2 cm is termed as an Ovarian Cyst. Other examples are Thecal Cysts and Corpus Luteum Cysts.
- Non-Functional Ovarian Cysts : These cysts do not arise from the female menstrual cycle. They can arise due to several other reasons, for example, Ovarian Cysts arising in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
Cause of Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian Cysts can arise from a number of reasons. Most common reason however is as follows :
As the Ovarian Follicle matures inside the ovary during a normal menstrual cycle, it grows in size. On the day of ovulation it ruptures and releases the egg outside to be carried to the Uterus via Fallopian tubes. However if it fails to rupture it forms a fluid filled structure with a thin wall covering and hence a Follicular Ovarian Cyst is formed.
Other reasons for formation of Ovarian Cysts are :
- Corpus Luteum is formed from ruptured follicle. If its size is more than 3 cm it is classified as Ovarian Cyst.
- Hormone abnormality may lead to formation of Thecal Cysts and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Endometriosis is proliferation of Uterine wall outside Uterus and it may result in formation of Ovarian Cysts.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian Cysts are mostly functional and harmless. Signs and Symptoms associated with the Ovarian Cysts are :
- Abdominal Pain
- Uterine Bleeding
- Rupture of Ovarian Cyst can cause sudden sharp pain on one side of the lower abdomen.
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Fatigue and Headaches are common
- Heaviness, Pressure or Bloating etc in the abdomen
- Difficulty in Urination
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cyst
The Ovarian Cysts occur in almost in all normal females. Risk Factors are mentioned below :
- Through research it is found out that the major risk factor is the Age. Women of childbearing age are susceptible.
- Family history in form of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome or Hormonal imbalance etc.
- Another factor is use of fertility or contraceptive drugs. Both these drug groups are related with increased Ovarian Cysts.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cyst
Diagnosis is made in step wise fashion as follows :
- Clinical History of the Patient
- Clinical examination by Doctor
- Ultrasonography (if above two indicate Ovarian Cyst)
- MRI and CT scan are useful for advanced studies and further investigations but only used if Doctor recommends it.
Further testing may be done to confirm diagnosis or check for complications like Cancer. These include :
- CA-125 test is a Blood test to check Cancer Antigens (particles related with cancer). This test is designed to check whether Ovarian Cyst is malignant or not.
- Several Hormone level tests can be done.
- Pregnancy test can be performed
Prevention from Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian Cysts are common in almost all females of the Childbearing age. However if a female is not planning on getting pregnant and feels uncomfortable with these Cysts she can prevent developing them. It is done by taking simple medication in form of Birthcontrol pills. These pills stop formation and proliferation of Ovarian Follicles. Hence Ovarian Cysts are not formed as they do with normal Menstrual Cycle.
Treatment of Ovarian Cyst
As the Ovarian Cysts are a normal phenomena hence usually no particular treatment is required for normal Functional Ovarian Cysts. To relieve symptoms like pain etc following measures can be taken :
Pain Relieving Medication can be used. Most commonly used are Paracetamol and Ibuprofen etc.
Warmth applied to the Lower Abdomen in form of heating pads, warm bath or hot water bottle etc can relax the muscles of the abdomen. This results in decrease in tension and discomfort and increase in blood flow and healing of ovaries.
In case of complicated Ovarian Cysts (cause symptoms, or are Non-Functional or very large in size or Malignant etc.) Surgery is required.
