Parkinson’s Disease
Definition of Parkinson’s Disease
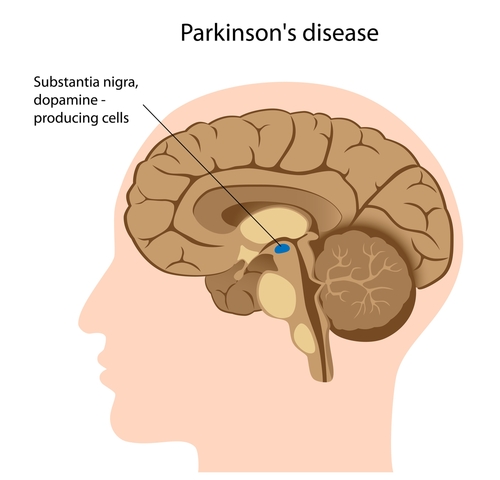
Parkinson’s disease is known by several names like paralysis agitans, hypokinetic rigidity syndrome and idiopathic parkinsonism. This is a disease that involves the degradation of certain portions of central nervous system. This pathology most commonly affects the dopamine system of human body. Dopamine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter of central and peripheral nervous system. Parkinsonism develops due to the degradation of dopamine generating cells present in substantia nigra, a portion of brain.
Cause of Parkinson’s Disease
The exact cause of this condition is mostly unknown i.e. this condition is idiopathic in majority cases. But some researches have attributed parkinsonism to be an amalgam of following causes.
-
Exposure to pesticides.
-
Some kind of injury to head.
-
Family history of this disease. You’re more prone to develop this condition if someone in your blood relations has got this disease. Genetic mutations mostly in following genes:
-
SNCA.
-
PARK2.
-
PARK7.
-
PINK1.
-
LRRK2.
-
Signs and Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms usually appear on one side of the body and with the passage of time continue to get worse. With the passage of time symptoms start to appear on the opposite side of the body as well. The symptoms usually appear due to the deficiency of dopamine. Following are the most important symptoms seen during the course of this disease.
-
Tremors.
-
Slowed movements of body parts (Bradykinesis).
-
Excessive rigidity of muscles.
-
Abnormal posture.
-
Abnormal gait.
-
Impaired ability to carry out automatic movement.
-
Slurred speech.
-
Changes in writing.
Risk Factors for Parkinson’s Disease
The risk factors for this disease include:
-
This disorder is most common in older adults. You’re more prone to develop this condition if you’re 60 years old or more.
-
If your blood relations have got this condition you’re are a higher risk to develop this condition yourself.
-
Parkinson’s disease is gender specific. Males are more prone to develop this condition as compared to females.
- If you’re living in a countryside where you’re being exposed to pesticide toxins, you’re highly likely to develop this condition.
Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease
There is no specific test that could diagnose parkinson’s disease. However, the symptoms of this disease do overlap with other mental ailments. To rule out the chances of other mental diseases, your doctor might order some tests.
The diagnosis of parkinsonism can be made by a professional neurologist. Following are the points that can help develop a diagnosis.
-
Complete history.
-
Clinical examination with particular emphasis on neurological and physical symptoms.
-
If a preliminary diagnosis is made, your doctor might suggest you a carbidopa-levodopa drugs. If your symptoms improve significantly it is a strong indicative that you’re suffering from parkinson’s disease.
Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
Till now no medication or surgical procedure has been devised that could totally cure this condition. All the surgeries done or medicines prescribed are meant to limit the symptoms of this illness.
The medicines that are most commonly used for the treatment of parkinson’s disease include the following:
-
Carbidopa-levodopa.
-
Dopamine agonists.
-
MAO-B inhibitors.
-
COMT inhibitors.
-
Amantadine.
-
Anticholinergic drugs.
The surgical procedures done include deep brain stimulation in which the portions of brain involved in the synthesis of dopamine are electrically stimulated so that they can release a higher level of dopamine.