Ulcerative Colitis
Definition of Ulcerative Colitis
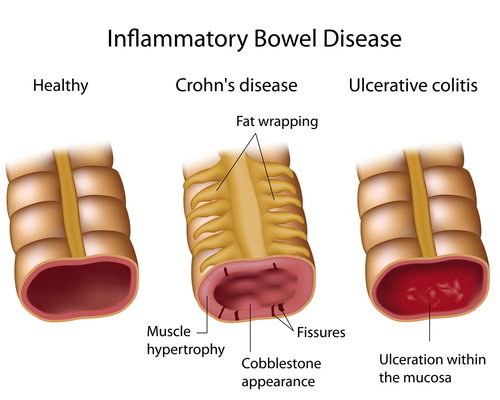
Ulcerative colitis means inflammation of colon (large intestine) in which ulcers or small sores are formed. Usually the lower part of digestive tract which includes large intestine and rectum are affected. It is a chronic disease and generally included in inflammatory bowel disease. The inflammation starts from the rectum and ascends upwards but remains below the small intestine. This chronic condition sometimes becomes fatal if left untreated. Intermittent phases of symptomatic and nonsymptomatic disease are seen. Due to inflammation, contents of bowel move rapidly and frequent emptying of bowel occurs. Hence, the patient presents with diarrhea mostly. The lining of digestive tract is affected and small ulcers are formed. As a result, often pus and mucus are discharged with stools and sometimes bleeding is also seen.
Cause of Ulserative Colitis
The definitive cause of ulcerative colitis is still unknown. However, various theories are proposed to explain the disease. These include the following causes:
Genetic causes : Research has shown that a person tends to develop ulcerative colitis if any other member of the family is already suffering from this disease. It is also seen that it is more common in some particular races like Caucasians.
Immune system : Studies have shown that immune system starts over working if it is triggered by any bacterial or viral infection. Colon is infiltrated by T cells of immune system. Ulcerative colitis is also considered as autoimmune disease because sometime there is no pathogen and immune system starts fighting against digestive tract’s own cells.
Effect of drugs : Research has shown a link between the users of a drug named as Isotretinoin and ulcerative colitis. This drug is used to treat cystic acne.
Signs And Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Following sign and symptoms if persist for a long time, these are indicative of ulcerative colitis.
 Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain- Bloody stools
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Increased abdominal sounds
- Rectal pain
- Weight loss
- Malnutrition
- Anemia
- Joint pain
- Joint swelling
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Skin ulcers
- Mouth sores
Risk Factors for Ulcerative Colitis
There are not any specific risk factors for ulcerative colitis. However there are more chances of occurrence of the disease due to following reasons :
- Age of 40 to 50
- Ethnicity
- Use of Isotretinoin
Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis
Following tests help finding the inflammation and extent of the ulcerative colitis.
- Stool examination
- Endoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Biopsy of colon
- Barium enema
- Complete blood examination
- C reactive protein test
Prevention from Ulcerative Colitis
Some following practices may help in preventing ulcerative colitis in high risk people
- Drink adequate water throughout the day at intervals
- Have small meals during whole day instead of having large meal at one time
- Don’t take high fiber foods too much
- Avoid foods with high fat content
- Lactose intolerant people should lower their milk intake
Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
Treatment plan involves therapy to relieve symptoms and to prevent the remission of disease. In mild and moderate forms of disease, medications will help but in severe form surgery has to be performed.
Following drugs are useful :
Anti inflammatory drugs : These include sulfasalazine, Mesalamine, balsalazide, Osalazine and corticosteroids.
Immune suppressors : These include cyclosporine, azathioprine, mercaptopurine, infliximab and adalimumab.
Other drugs : These include pain relievers, antidiarrheals and antibiotics.
In surgical procedures, two type of surgeries are performed :
Proctocolectomy with ileostomy : In this type of surgery, colon and rectum is removed. The terminal part of ileum is connected to an opening made in abdominal cavity. Hence waste material is then drained by a bag attached to it.
Ileoanal anastomosis : In this procedure, only colon is removed and ileum is connected to the rectum.
