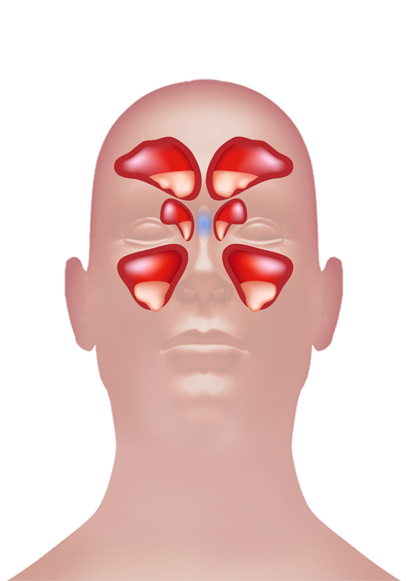
Sinus Sphenoidalis
In the anatomy of the head and neck you will find the sinus sphenoidalis. Although these paired sinuses vary in size and shape they may be quite large or not present at all. They can become displaced by the intervening septum and are rarely symmetrical. Each sinus develops after puberty and enlarges; until then, they are small.
read more Sinus Frontalis Superior Nasal ConchalInferior Nasal Concha Nasal CavitySinus Sphenoidalis Alveoli Larynx Nasopharynx
Oropharynx Laryngopharynx Frontal SinusSphenoid SinusEthmoid Sinus Maxillary SinusBronchus Vertebrate Trachea Bronchioles Capillary Beds
Alveolar Duct Alveolar Sacs Pulmonary VeinPulmonary Artery
Sinus Sphenoidalis
Each sinus opens into the roof of the nasal cavity through apertures on the posterior wall of the sphenoethmoidal recess directly above the choana. The choana receives the opening of the sphenoidal sinus. The choana is part of a system that moves mucus that has been collected by the sinuses which are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull.
Nasal and sinus mucosa are ciliated (hair-like fingers) and move mucus to the choanae and finally to the stomach. The thick upper layers of nasal mucus trap bacteria and small particles in tissue that has many immune cells, antibodies, and antibacterial proteins. The layers beneath are thinner and have cilia which are able to beat and move the upper layer with its debris through the ostia toward the choanae.
The maxillary sinus consists of the maxilla, the frontal, the ethmoid , and the sphenoid bones. These three combine to be the largest sinus made up of the frontal sinus, the ethmoid sinus, and the sphenoid sinus. The sphenoid sinus is located in the upper posterior wall of the nasal cavity at the back of the nose.
The sinuses have two functions which are to be filled with air and to help keep the weight of the skull balanced. The sphenoid sinuses are situated at the forward part of the skull that forms the fossa for the pituitary gland. The bony wall (septum) that separates them is irregular and not midline to the skull, and they discharge their mucus through an opening in the front wall of the sinus (choana) into the nose. The conchae are made up of the turbinate bones which have a superior, middle and inferior bony ridges that make up the nasal cavity and are part of the respiratory system. However, the anatomy of the sphenoidal sinus is part of the paranasal air sinuses.
Report Error